Polar Bears vs Humans: A Fascinating Comparison
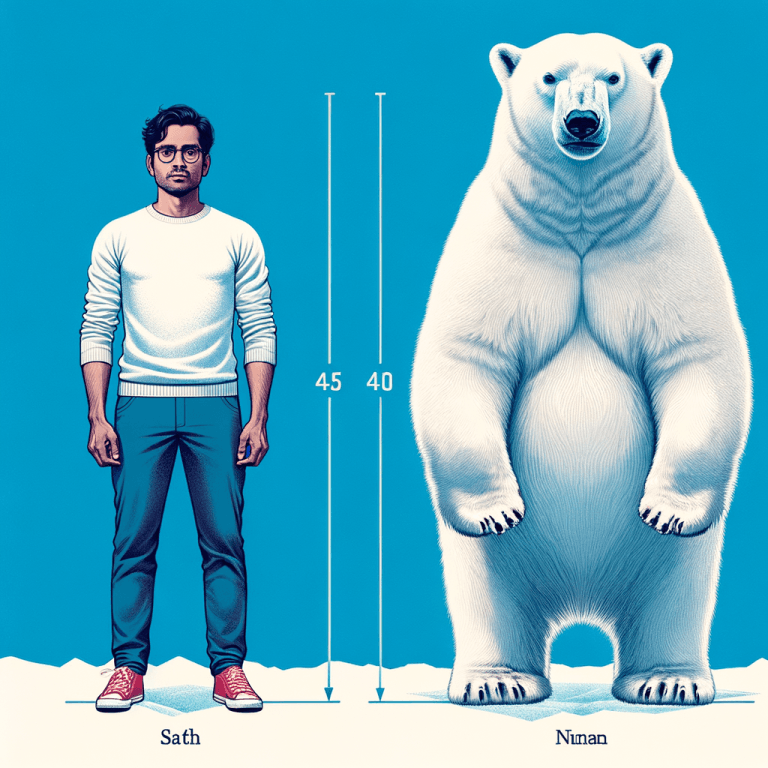
When comparing polar bears to humans, it’s important to note their physical characteristics, behavioral contrasts, geographical locations, and interesting facts and figures. Polar bears can weigh up to 1,500 pounds (680 kg) and stand over 10 feet (3 meters) tall, while the average human weighs around 137 pounds (62 kg) and stands at 5.6 feet (1.7 meters) tall. Their diet and hunting habits, as well as their habitat and lifestyle, differ greatly from those of humans.
Discover the Astonishing Size of a Polar Bear Compared to a Human
Find out just how massive a polar bear is in comparison to the average human, and prepare to be amazed by the incredible size difference between these two species.
Physical Characteristics
When it comes to physical characteristics, polar bears are truly impressive creatures. Standing at an average height of 8 to 10 feet (2.4 to 3 meters) when on their hind legs, they tower over the average human, whose height typically ranges from 5 to 6 feet (1.5 to 1.8 meters). In terms of weight, polar bears can weigh anywhere from 900 to 1,600 pounds (410 to 720 kilograms), far exceeding the average human weight of 137 pounds (62 kilograms).
Comparison to average human height and weight:
- Polar bear height: 8 to 10 feet (2.4 to 3 meters) vs. Human height: 5 to 6 feet (1.5 to 1.8 meters)
- Polar bear weight: 900 to 1,600 pounds (410 to 720 kilograms) vs. Human weight: 137 pounds (62 kilograms)
Behavioral Contrasts
When it comes to behavior, polar bears and humans have stark differences. Polar bears primarily feed on seals and other marine mammals, relying on their hunting prowess and keen sense of smell to survive in their icy habitat. In contrast, humans have a much more varied diet, with a focus on agriculture and domesticated animals for sustenance. Additionally, polar bears lead a solitary lifestyle, while humans are known for their social nature and complex societal structures.
Variances in diet and hunting habits:
- Polar bears primarily feed on seals and marine mammals
- Humans have a varied diet, with a focus on agriculture and domesticated animals
Variances in habitat and lifestyle:
- Polar bears lead a solitary lifestyle in the Arctic
- Humans are known for their social nature and complex societal structures
Geographical Locations
Polar bears are predominantly found in the Arctic region, where they have adapted to the harsh, icy conditions. In contrast, humans are distributed across the globe, with the majority residing in more temperate climates. This stark difference in geographical distribution highlights the unique adaptability of polar bears to their extreme environment.
Comparison to human population distribution:
- Polar bears predominantly found in the Arctic region
- Humans distributed across the globe, with the majority residing in more temperate climates
Overall, the comparison between polar bears and humans naturally reveals the fascinating contrasts in physical characteristics, behavior, and geographical distribution. These differences underscore the remarkable adaptability of both species to their respective environments.
Behavioral Contrasts
When comparing polar bears to humans, it is important to consider their behavioral differences, which are influenced by their distinct habitats and lifestyles.
A. Differences in diet and hunting habits
Polar bears primarily feed on seals, relying on their hunting skills and patience to catch their prey. Their diet consists mainly of fat, which provides them with the energy needed to survive in their harsh environment. In contrast, humans have a more varied diet, consuming a wide range of foods including fruits, vegetables, and meats. Their hunting habits are also vastly different, as humans have developed various methods for obtaining food, such as farming, fishing, and hunting different types of animals.
B. Variances in habitat and lifestyle
Polar bears inhabit the Arctic region, where they have adapted to the extreme cold and vast expanses of ice. Their lifestyle revolves around the sea ice, which they use as a platform for hunting and traveling. In comparison, humans have established diverse habitats across the globe, ranging from tropical regions to polar areas. Their lifestyle is shaped by their ability to build shelters, cultivate crops, and utilize various resources to thrive in different environments.
 Geographical Locations
Geographical Locations
When it comes to geographical locations, polar bears are primarily found in the Arctic region, where they have adapted to the cold and icy environment. This includes areas such as Canada, Alaska, Greenland, Norway, and Russia. The distribution of polar bears is closely tied to the presence of sea ice, as they rely on it for hunting and traveling.
In comparison, the human population is spread across the globe, with the majority residing in urban and suburban areas. While humans have also adapted to various climates and environments, the distribution is much more widespread compared to the specific Arctic habitat of polar bears.
Facts and Figures
When it comes to polar bears, there are some interesting facts and figures that set them apart from humans. Let’s take a look at some of these:
Interesting Facts about Polar Bears
- Polar bears are the largest land carnivores in the world, with adult males weighing between 900 to 1,600 pounds (408 to 726 kilograms) and standing at a height of 8 to 10 feet (2.4 to 3 meters) when on their hind legs.
- They have a thick layer of blubber and a dense fur coat to insulate them from the cold Arctic temperatures.
- Polar bears are excellent swimmers, capable of covering long distances in search of food.
- They have a keen sense of smell, which helps them locate seals, their primary prey, even from a distance.
Statistical Comparisons to Human Population
- The estimated global population of polar bears is around 22,000 to 31,000 individuals, spread across the Arctic region.
- In contrast, the human population is over 7.8 billion, with a much wider distribution across the globe.
- While polar bears face threats such as climate change and habitat loss, humans also impact their environment through activities like oil and gas exploration in the Arctic.
- Both polar bears and humans are apex predators in their respective ecosystems, with significant impacts on the food chain.
These facts and figures highlight the unique characteristics and challenges faced by polar bears compared to humans, shedding light on the importance of understanding and protecting these magnificent creatures in their natural habitat.
Conclusion
The comparison between polar bears and humans reveals fascinating insights into the similarities and differences between these two species.
Recap of Key Points
– Polar bears are the largest land carnivores, with males reaching heights of up to 10 feet (3 meters) and weighing between 900 to 1,600 pounds (408 to 726 kilograms), while the average human male stands at 5 feet 9 inches (1.75 meters) and weighs 197.9 pounds (89.8 kilograms).
– Polar bears primarily feed on seals and fish, while humans have a diverse omnivorous diet.
– Polar bears inhabit the Arctic region, while humans are distributed across the globe.
Final Thoughts on the Comparison
While polar bears and humans share certain physical and behavioral characteristics, such as being apex predators and having complex social structures, their differences in diet, habitat, and lifestyle are significant. The comparison between polar bears and humans naturally highlights the diverse ways in which species adapt to their environments and thrive in their respective ecosystems. This comparison serves as a reminder of the importance of understanding and preserving the natural world and the unique roles that different species play within it.

Comments are closed.