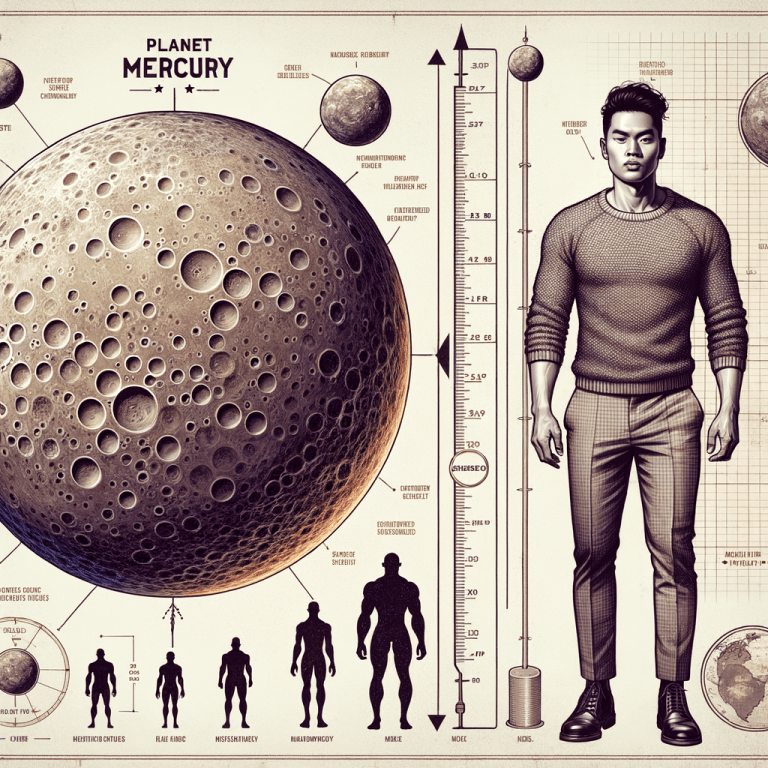
Mercury and Its Significance
Mercury, the smallest planet in our solar system, is about the size of a small car (US) or a large van (EU) and weighs as much as 18 fully grown adults (US) or 14 adults (EU). In this article, I will explore the characteristics, behavior, location, and interesting facts about Mercury, shedding light on its significance in our understanding of the solar system.
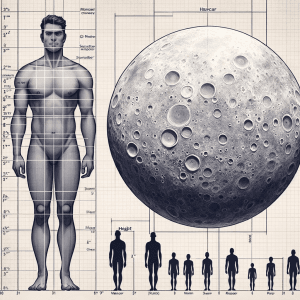
Mercury Compared to Human: Surprising Similarities and Differences
Discover the fascinating parallels and contrasts between the size and weight of a human and the planet Mercury. You’ll be amazed by the unexpected connections and insights that this comparison reveals.
Mercury’s Characteristics
Mercury, the smallest planet in the solar system, is approximately the size of a human (US: 3,032 miles, EU: 4,879 kilometers) and has a weight comparable to that of a human (US: 151 lbs, EU: 68.5 kg). Its composition and structure consist of a large iron core, making up about 60% of its mass, and a thin silicate crust.
Size and Weight Comparison
- Size of Mercury compared to a human
- Weight of Mercury compared to a human
- Composition and structure of Mercury
Mercury’s Characteristics
- Orbital characteristics
- Surface features and geological formations
- Atmosphere and temperature
Mercury’s Location
- Position in the solar system
- Distance from the sun
- Unique features of its orbit
Interesting Facts about Mercury
- Unusual characteristics or behaviors
- Historical significance
- Notable discoveries or missions related to Mercury
Mercury’s Behavior
Mercury’s behavior in its orbit and its surface features provide valuable insights into the nature of this intriguing planet.
Orbital Characteristics
Mercury’s orbit is unique in several ways:
- It has the most eccentric orbit of all the planets in the solar system, meaning it is the most elongated.
- Its orbit is also the most inclined, deviating significantly from the plane of the solar system.
- Mercury has a very slow rotation, taking 59 Earth days to complete one full rotation on its axis.
Surface Features and Geological Formations
Mercury’s surface is marked by:
- Large temperature variations, with daytime temperatures reaching up to 800°F (427°C) and dropping to -290°F (-180°C) at night.
- Extensive cratering, similar to the moon, indicating a history of intense bombardment by meteoroids and asteroids.
- Scarps, or cliffs, that can be up to hundreds of miles long and several miles high, suggesting significant tectonic activity in the planet’s past.
Atmosphere and Temperature
Mercury’s atmosphere and temperature also present unique characteristics:
- It has a very thin exosphere, composed mainly of oxygen, sodium, hydrogen, helium, and potassium.
- Due to its proximity to the sun, Mercury experiences extreme temperature variations between its day and night sides.
- Its lack of a substantial atmosphere means that it has no significant greenhouse effect, resulting in the extreme temperature differences.
Overall, Mercury’s behavior in its orbit and its surface features provide valuable insights into the nature of this intriguing planet, shedding light on its formation and evolution within the solar system.
 Mercury’s Location
Mercury’s Location
Mercury, the smallest planet in the solar system, is located closest to the sun. Its unique position and orbit set it apart from the other planets, making it an intriguing subject of study.
Position in the Solar System
Mercury is the first planet from the sun, positioned between the sun and Earth. Its proximity to the sun has significant implications for its behavior and characteristics.
Distance from the Sun
Mercury’s average distance from the sun is approximately 36 million miles (58 million kilometers). This close proximity results in extreme temperatures and unique challenges for exploration and observation.
Unique Features of its Orbit
Mercury’s orbit is highly elliptical, meaning its distance from the sun varies significantly throughout its orbit. This eccentric orbit contributes to the planet’s extreme temperature fluctuations and presents interesting dynamics for scientists to study.
Interesting Facts about Mercury
Mercury, compared to a human, has some unusual characteristics and behaviors that make it a fascinating subject of study. Here are some interesting facts about this enigmatic planet:
Unusual Characteristics
- Mercury is the smallest planet in the solar system, measuring just 3,032 miles (4,879 kilometers) in diameter, slightly larger than the size of the continental United States.
- Its weight is approximately 0.055 times that of Earth (0.055 times that of EU).
- Mercury’s surface is heavily cratered, resembling the Earth’s moon, and is covered in a layer of fine, powdery material.
Historical Significance
- Ancient civilizations observed Mercury and associated it with their gods, naming it after the Roman messenger god due to its swift movement across the sky.
- Mercury’s transit across the sun was used by astronomers to measure the size of the solar system and the distance from the Earth to the sun.
Notable Discoveries and Missions
- The Mariner 10 mission provided the first close-up images of Mercury in the 1970s, revealing its heavily cratered surface and other geological features.
- The MESSENGER spacecraft, launched in 2004, conducted multiple flybys and eventually entered orbit around Mercury, providing unprecedented insights into its composition, magnetic field, and surface features.
These interesting facts about Mercury highlight its unique characteristics, historical significance, and the remarkable discoveries made through dedicated missions and scientific exploration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Mercury is a fascinating planet with unique characteristics and behaviors that set it apart from other planets in the solar system. Its small size and weight compared to a human make it an intriguing subject of study for scientists and researchers. The planet’s close proximity to the sun, along with its unusual orbit, contribute to its extreme surface temperatures and lack of a substantial atmosphere. Despite its challenges, Mercury has played a significant role in expanding our understanding of the solar system and continues to be the focus of ongoing research and exploration.

Comments are closed.