Exploring the Similarities and Differences Between Sheep and Human Brains
Comparing sheep brains and human brains is crucial for understanding the complexities of the human brain. The physical characteristics of a sheep brain differ from those of a human brain, but there are also striking similarities in the structures and functions. As we delve into this comparison, we uncover fascinating insights into the intricate workings of both species’ brains.
Discovering Surprising Similarities
Read on to uncover the fascinating similarities between sheep brains and human brains, and how this comparison can provide valuable insights into the human mind.
Anatomy of Sheep Brain
When comparing sheep brains and human brains, it is important to understand the physical characteristics of a sheep brain and how they differ from those of a human brain. Some key points to consider include:
- Description of the physical characteristics of a sheep brain
- Comparison to the anatomy of a human brain
- Highlighting specific structures and their functions
Description of the physical characteristics of a sheep brain
The average weight of a sheep brain is around 140 grams (0.14 kg), which is significantly smaller than the average weight of a human brain, which is about 1,400 grams (1.4 kg). The sheep brain also has a different overall shape and structure compared to the human brain.
Comparison to the anatomy of a human brain
While both sheep and human brains share some common structures, such as the cerebellum and cerebral cortex, there are also distinct differences in size and specific regions of the brain.
Highlighting specific structures and their functions
Specific structures in the sheep brain, such as the olfactory bulb, play a crucial role in the animal’s sense of smell, which differs from the human brain’s olfactory system. Understanding these differences can provide valuable insights into the sensory capabilities of both species.
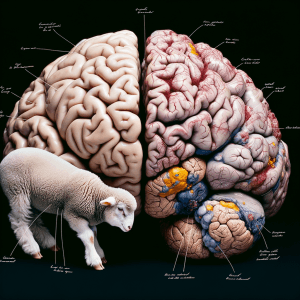 Anatomy of Human Brain
Anatomy of Human Brain
When comparing sheep brains and human brains, it is essential to understand the physical characteristics of the human brain. The human brain is approximately 3 pounds (1.36 kg) in weight and has a more complex structure compared to the sheep brain. It consists of distinct regions, including the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem, each with specific functions.
Comparison to the Anatomy of a Sheep Brain
Compared to the sheep brain, the human brain is larger in size and has a more developed cerebral cortex, which is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as thinking, memory, and language. Additionally, the human brain has a more pronounced frontal lobe, which plays a crucial role in decision-making and social behavior.
Highlighting Specific Structures and Their Functions
Specific structures in the human brain, such as the hippocampus and amygdala, are responsible for memory and emotional processing, respectively. These structures are more advanced in the human brain compared to the sheep brain, reflecting the differences in cognitive and emotional capabilities between the two species.
Behavioral Differences
When comparing sheep brains and human brains, it is important to consider any potential behavioral differences that may arise due to differences in brain anatomy. While sheep and humans share some similarities in behavior, there are also distinct differences that can be attributed to their brain structures.
Explanation of Behavioral Differences
Sheep are known for their flocking behavior, which is a natural instinct that allows them to seek safety in numbers and follow a leader. This behavior is influenced by the structure of the sheep brain, particularly the areas responsible for social interaction and group dynamics. In contrast, humans exhibit a wider range of behaviors influenced by the complexity of the human brain, including advanced social interactions, problem-solving, and emotional responses.
Discussion of Similarities in Behavior
Despite the differences in brain anatomy, there are also similarities in behavior between sheep and humans. Both species display social behaviors, form bonds with others, and exhibit responses to environmental stimuli. These similarities highlight the interconnectedness of brain function and behavior across different species.
Geographical Distribution
When comparing sheep brains and human brains, it is important to consider the geographical distribution of both species. This can have an impact on brain development and function, as well as certain behaviors.
A. Overview of where sheep and humans are commonly found
Sheep are commonly found in various regions around the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. They are often raised for wool, meat, and milk production, and their distribution is influenced by factors such as climate, vegetation, and human agricultural practices.
On the other hand, humans are found in nearly every corner of the globe, with diverse populations inhabiting different environments, from densely populated urban areas to remote rural regions. The distribution of humans is influenced by factors such as historical migration patterns, economic opportunities, and cultural preferences.
B. Impact of geographical location on brain development and function
The geographical distribution of sheep and humans can impact brain development and function in several ways:
- Environmental factors such as climate and altitude can influence brain development in both species, potentially leading to adaptations for survival in specific environments.
- Cultural practices and traditions related to food, social interactions, and education can also shape brain function and behavior in both sheep and humans.
- Access to resources and exposure to different stimuli can vary based on geographical location, potentially affecting brain development and cognitive abilities.
Understanding the impact of geographical distribution on brain development and function is essential for gaining a comprehensive understanding of the similarities and differences between sheep brains and human brains.
Facts and Figures
When comparing sheep brains and human brains, it is important to consider the statistical data on the size and weight of these organs. Here are some key facts and figures related to brain comparison:
A. Size and Weight
According to research, the average weight of a sheep brain is approximately 140 grams (0.31 lbs), while the average weight of a human brain is around 1,400 grams (3.09 lbs). This significant difference in weight is due to the larger size of the human brain compared to that of a sheep.
Additionally, the average size of a sheep brain is about 7-8 cm in length, 4-5 cm in width, and 4-5 cm in height. In contrast, the average size of a human brain is approximately 15 cm in length, 13 cm in width, and 11 cm in height. These measurements further illustrate the notable disparities in size between sheep and human brains.
B. Other Relevant Facts
Aside from size and weight, there are other relevant facts to consider when comparing sheep brains and human brains:
- Sheep brains have a simpler convoluted surface compared to the highly convoluted surface of human brains, which allows for increased surface area and capacity for cognitive functions.
- Human brains have a larger prefrontal cortex, which is associated with higher cognitive functions such as decision-making, problem-solving, and social behavior, while sheep brains have a smaller prefrontal cortex in comparison.
- The ratio of brain size to body size is higher in humans than in sheep, indicating a greater emphasis on cognitive abilities in humans.
These facts and figures provide valuable insights into the differences in size, structure, and cognitive capabilities between sheep brains and human brains, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comparison of sheep brains and human brains provides valuable insights into the similarities and differences between the two. Understanding these differences and similarities is crucial for scientific and educational purposes.
Key points discussed in the article include:
- The physical characteristics of sheep brains and human brains, highlighting specific structures and their functions
- Behavioral differences and similarities related to brain anatomy
- Geographical distribution and its potential impact on brain development and function
- Facts and figures, such as statistical data on the size and weight of sheep brains compared to human brains
It is important to note that the comparison of sheep brains and human brains offers valuable insights into brain anatomy and function. This information can be used to further scientific research and enhance educational understanding of the brain.
By providing a comprehensive guide to the comparison of sheep brains and human brains, this article aims to inform and educate readers about the key similarities and differences between the two. The clear and organized structure, along with the use of simple and accessible language, ensures that the information is easily understandable for a general audience interested in learning about this topic.


Comments are closed.