Anatomy and Function of Horse Lungs Compared to Humans
Understanding the differences in lung structure and function between horse and human lungs is crucial for their care and management. Horse lungs are larger and have a more efficient oxygen exchange system compared to human lungs, allowing them to excel in athletic activities. It’s fascinating to explore how these differences impact their respiratory process and overall health.
Discover the Astonishing Comparison Between Horse Lungs and Human Lungs
If you’ve ever wondered how the respiratory system of a horse stacks up against that of a human, this article will provide you with fascinating insights that will leave you amazed. From size and capacity to efficiency, you’ll be surprised by the similarities and differences between these two species.
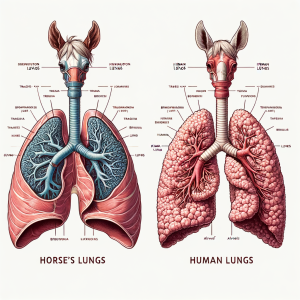
Anatomy of Horse Lungs
When comparing horse lungs to human lungs, it is important to note that horse lungs are larger and have a different structure. The anatomy of horse lungs allows for efficient oxygen exchange due to their unique characteristics:
- Horse lungs are larger in size compared to human lungs, with a capacity of approximately 1800-4500 liters (64-159 cubic feet) compared to 4-6 liters (0.14-0.21 cubic feet) in humans.
- The structure of horse lungs includes a larger surface area for gas exchange, with a higher number of alveoli, which are small air sacs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
- Horse lungs have a greater capacity for oxygen uptake, allowing them to meet the demands of their athletic activities.
These anatomical differences contribute to the exceptional respiratory capabilities of horses, enabling them to perform strenuous activities such as racing and jumping.
Function of Horse Lungs
When comparing horse lungs to human lungs, it is important to understand the respiratory process in horses. The respiratory process in horses involves the intake of air through the nostrils, which then travels through the nasal passages, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and into the lungs. The unique adaptations of horse lungs allow for efficient oxygen exchange, enabling them to meet the high oxygen demands of their athletic activities.
Comparing this to the human respiratory process, both species share the basic process of inhaling and exhaling air, but the anatomical differences in horse lungs allow for a more rapid exchange of gases, making them well-suited for their athletic abilities.
 Differences in Lung Capacity
Differences in Lung Capacity
When comparing horse lungs to human lungs, one of the most significant differences lies in lung capacity. Horses have a much larger lung capacity compared to humans, allowing them to take in a greater volume of air with each breath. This increased lung capacity is a crucial adaptation for their athletic abilities and overall performance.
Here are some key points to consider when examining the differences in lung capacity between horses and humans:
- Horse lung capacity is approximately 70 liters (70,000 ml), while human lung capacity is around 6 liters (6,000 ml).
- The larger lung capacity in horses enables them to maximize oxygen intake during strenuous physical activities, such as racing and jumping.
- This increased capacity also allows for more efficient removal of carbon dioxide, a byproduct of respiration, during intense exercise.
- Understanding these differences in lung capacity is essential for evaluating and optimizing the athletic performance and endurance of horses.
Common Respiratory Issues in Horses
When it comes to respiratory health, horses can face a variety of common issues that can impact their overall well-being and performance. Understanding these issues is crucial for proper care and management of these majestic animals. Here are some of the most prevalent respiratory conditions in horses:
Common Conditions
- Heaves (Recurrent Airway Obstruction): This chronic condition is similar to asthma in humans and can cause coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. It is often triggered by environmental factors such as dust and allergens.
- Equine Influenza: Just like humans, horses can also suffer from the flu. Equine influenza can spread rapidly in a herd and lead to symptoms such as fever, coughing, and nasal discharge.
- Strangles: This highly contagious bacterial infection affects the upper respiratory tract and can cause abscesses and difficulty swallowing. It is important to isolate infected horses to prevent the spread of the disease.
Comparison to Human Respiratory Issues
While some respiratory issues in horses may have similarities to those in humans, the specific conditions and their impact on the animals can differ significantly. For example, heaves in horses is more closely related to allergic airway disease in humans, but the triggers and management strategies can vary between the two species. Equine influenza, on the other hand, shares similarities with human influenza in terms of symptoms and transmission, but the strains of the virus are specific to each species.
It is important to note that proper lung function is essential for the overall health and performance of horses. Respiratory issues can significantly impact their athletic abilities and quality of life, making it crucial for horse owners and caretakers to be vigilant about monitoring and managing their respiratory health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comparison between horse lungs and human lungs highlights the unique adaptations and differences in lung structure and function. Understanding these differences is crucial for the care and management of horses, as well as for gaining insights into their athletic abilities. The respiratory system of horses plays a vital role in their overall health and performance, making it essential for horse owners, trainers, and veterinarians to have a comprehensive understanding of their respiratory anatomy and function.
By recognizing the distinct characteristics of horse lungs compared to human lungs, individuals involved in the care of horses can make informed decisions regarding their health and well-being. This knowledge can also contribute to the development of effective training and management strategies to optimize the respiratory health and performance of horses.
Overall, the differences and similarities between horse and human lungs underscore the importance of tailored approaches to respiratory care and management in horses. By acknowledging and addressing these unique aspects, individuals can ensure the well-being and athletic potential of these remarkable animals.

Comments are closed.