Understanding Neanderthals and Their Significance
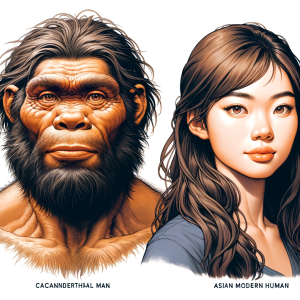
When comparing Neanderthals to modern humans, it’s fascinating to note the differences in physical appearance, such as their stockier build and shorter stature (160-170 cm). Their hunting and gathering practices, as well as their social structures and communication, also set them apart from us. Exploring these variations helps us better understand the genetic, cultural, and technological differences between Neanderthals and humans today.
Neanderthal Compared to Human: Surprising Similarities and Differences
Discover the fascinating similarities and differences between Neanderthals and modern humans, and how they stack up against other animals, buildings, and objects. You won’t believe the surprising findings!
Physical Characteristics
When comparing Neanderthals to modern humans, there are several notable differences in physical appearance:
- Neanderthals were generally shorter and stockier than modern humans, with an average height of 5’5″ (165 cm) for males and 5’1″ (155 cm) for females.
- They also had a more robust skeletal structure, with a larger and more muscular build compared to the lighter, more gracile structure of modern humans.
Behavioral Differences
Neanderthals and modern humans also exhibited differences in their hunting and gathering practices:
- Neanderthals were primarily big-game hunters, relying on close-range hunting techniques to take down large prey such as mammoths and bison.
- Modern humans, on the other hand, were more versatile in their hunting strategies, utilizing long-range weapons and a wider variety of prey.
In terms of social structures and communication, Neanderthals are believed to have lived in smaller, more isolated groups compared to the larger, more interconnected communities of modern humans.
Geographic Distribution
Neanderthals inhabited regions of Europe and parts of western Asia, while modern humans have a much broader distribution across the globe, including Africa, Asia, Europe, Australia, and the Americas.
Genetic Variations
Studies have shown that Neanderthals and modern humans have genetic differences, with modern humans carrying a small percentage of Neanderthal DNA in their genome. This suggests some level of interbreeding between the two groups.
Cultural and Technological Differences
Neanderthals were known for their use of Mousterian stone tools and had a more limited artistic and symbolic expression compared to modern humans, who developed more advanced tools and engaged in complex artistic endeavors.
Behavioral Differences
When comparing Neanderthals to modern humans, there are several notable differences in behavior that provide insight into their way of life.
Hunting and Gathering Practices
Neanderthals were skilled hunters and relied heavily on large game for sustenance. Their hunting techniques involved close-range attacks using spears and other tools, indicating a high level of physical strength and coordination. In contrast, modern humans utilized a more diverse range of hunting and gathering strategies, including the use of traps and a wider variety of food sources.
Social Structures and Communication
Neanderthals lived in small, close-knit groups and likely had complex social structures. Evidence suggests that they cared for the sick and elderly within their communities, indicating a level of compassion and cooperation. In terms of communication, Neanderthals are believed to have used a combination of vocalizations, gestures, and possibly even symbolic language. Modern humans, on the other hand, developed more sophisticated forms of communication, including language and symbolic expression, which likely contributed to their ability to form larger, more interconnected societies.
 Geographic Distribution
Geographic Distribution
Neanderthals were primarily found in Europe and parts of western Asia, with evidence of their presence in regions such as present-day France, Spain, Germany, and the Middle East. Their distribution was more localized compared to modern humans, who have spread across the globe.
When comparing the geographic distribution of Neanderthals to modern humans, it is evident that Neanderthals were confined to specific regions, while modern humans have established populations on every continent.
Genetic Variations
Neanderthals and modern humans exhibit significant genetic differences, which have important implications for our understanding of human evolution and genetics.
A. DNA differences between Neanderthals and modern humans
Research has shown that Neanderthals and modern humans share a common ancestor, but also have distinct genetic variations:
- Neanderthals have a higher percentage of Neanderthal DNA compared to modern humans, with estimates ranging from 1-4% in non-African populations.
- Modern humans have specific genetic mutations that are not present in Neanderthals, particularly in genes related to brain development and cognitive function.
- Neanderthals also had genetic adaptations to their environment, such as genes related to immune response and metabolism, which differ from those found in modern humans.
B. Impact on modern human genetics
The genetic variations between Neanderthals and modern humans have had a lasting impact on the genetic diversity of modern human populations:
- Interbreeding between Neanderthals and modern humans has contributed to the genetic diversity of modern human populations, particularly in non-African populations.
- Some of the genetic variations inherited from Neanderthals have been associated with traits such as skin and hair color, immune response, and susceptibility to certain diseases.
- Studying the genetic differences between Neanderthals and modern humans provides valuable insights into the evolutionary history and genetic diversity of our species.
Overall, the genetic variations between Neanderthals and modern humans offer a fascinating glimpse into the complex tapestry of human evolution and genetics, shedding light on the shared history and unique characteristics of our species.
Cultural and Technological Differences
When comparing Neanderthals to modern humans, it is important to consider the cultural and technological differences that existed between the two groups. These differences provide valuable insights into the ways in which Neanderthals interacted with their environment and each other.
A. Tools and Technology
Neanderthals were known for their use of stone tools, which they crafted with precision and skill. These tools were essential for hunting, but also for other tasks such as cutting and scraping. The tools used by Neanderthals were well-adapted to their needs and were an important part of their survival strategy. In comparison, modern humans also used stone tools, but they were more advanced in their techniques and were able to create a wider variety of tools for different purposes.
B. Artistic and Symbolic Expression
One of the most intriguing aspects of Neanderthal culture is their artistic and symbolic expression. While it was once believed that Neanderthals were not capable of creating art, recent discoveries have challenged this notion. Evidence of cave paintings, jewelry, and other symbolic artifacts suggests that Neanderthals had a rich and complex culture. In comparison, modern humans also created art and symbolic objects, but their artistic expression was more diverse and sophisticated.
Overall, the cultural and technological differences between Neanderthals and modern humans provide valuable insights into the ways in which these two groups interacted with their environment and expressed themselves. By understanding these differences, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of human evolution and the ways in which our ancestors adapted to their surroundings.
Conclusion
Neanderthals, compared to modern humans, were a distinct species with their own unique physical, behavioral, genetic, and cultural characteristics. Understanding these differences is crucial in gaining a comprehensive understanding of human evolution and the development of modern human societies. By comparing Neanderthals to modern humans, we can gain valuable insights into the factors that shaped our species and the traits that make us unique.
It is important to note that despite these differences, Neanderthals and modern humans also shared many similarities. Both species were capable of complex tool use, had social structures, and communicated with each other. By recognizing these similarities, we can appreciate the commonalities that connect us to our ancient ancestors.
Overall, the study of Neanderthals provides a fascinating glimpse into the complexities of human evolution and the diverse paths that different human species have taken. By examining the differences and similarities between Neanderthals and modern humans, we can gain a deeper understanding of our own species and the rich tapestry of human history.


Comments are closed.